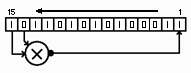
A LFSR (linear feedback shift register) is a shift register where the input is a linear function of two or more bits (taps). There are many possible configurations, the one presented here is very simple and has the property that it will start from an input of all 0's and is very easy to implement in software and hardware.
A LFSR of this type will never contain only 1's and would stall if loaded with that value. Only some taps will generate a maximal sequence with a period of 2^n-1 cycles.
If you need a counter and it does not have to count in a linear way then a LFSR is faster and requires less hardware resources.
Some possible uses:
Pseudo random number generator
Head and tail pointers in a FIFO
Program counter in a simple CPU
http://mathworld.wolfram.com/FiniteField.html
A simple simulation of a LFSR with two taps: lfsrsim.zip